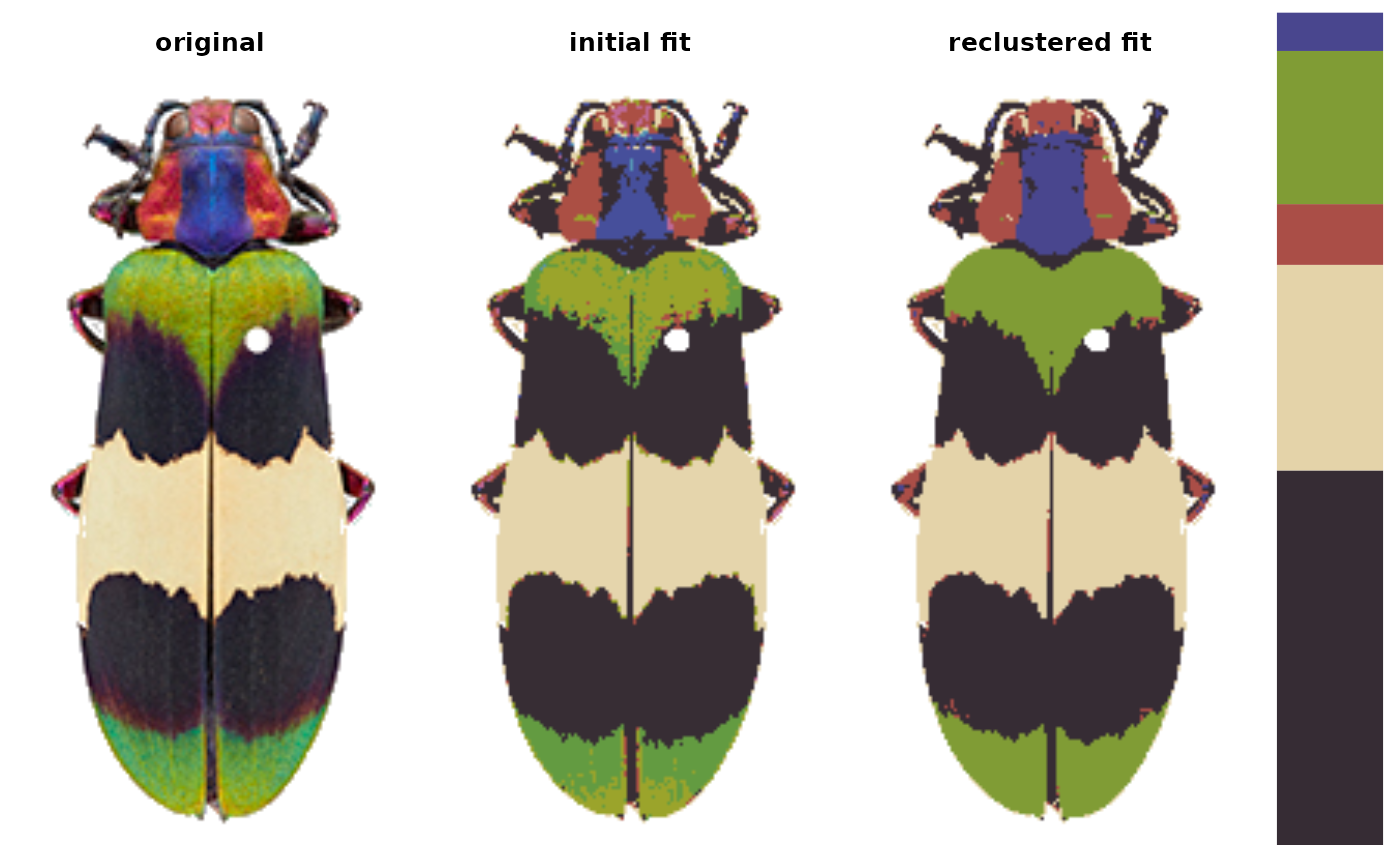
Calls recolorize and recluster in sequence, since these are often very effective in combination.
Usage
recolorize2(
img,
method = "histogram",
bins = 2,
n = 5,
cutoff = 20,
channels = 1:3,
n_final = NULL,
color_space = "sRGB",
recluster_color_space = "Lab",
refit_method = "impose",
ref_white = "D65",
lower = NULL,
upper = NULL,
transparent = TRUE,
resize = NULL,
rotate = NULL,
plotting = TRUE
)Arguments
- img
Path to the image (a character vector) or a 3D image array as read in by
png::readPNG(){readImage}.- method
Method for clustering image colors. One of either
histogramorkmeans. See details.- bins
If
method = "histogram", either the number of bins per color channel (if a single number is provided) OR a vector of length 3 with the number of bins for each channel.- n
If
method = "kmeans", the number of color clusters to fit.- cutoff
Numeric similarity cutoff for grouping color centers together. The range is in absolute Euclidean distance. In CIE Lab space, it is greater than 0-100, but cutoff values between 20 and 80 will usually work best. In RGB space, range is 0-sqrt(3). See recluster details.
- channels
Numeric: which color channels to use for clustering. Probably some combination of 1, 2, and 3, e.g., to consider only luminance and blue-yellow (b-channel) distance in CIE Lab space, channels = c(1, 3 (L and b).
- n_final
Final number of desired colors; alternative to specifying a similarity cutoff. Overrides
similarity_cutoffif provided.- color_space
Color space in which to minimize distances, passed to
[grDevices]{convertColor}. One of "sRGB", "Lab", or "Luv". Default is "sRGB".- recluster_color_space
Color space in which to group colors for reclustering. Default is CIE Lab.
- refit_method
Method for refitting the image with the new color centers. One of either "impose" or "merge".
imposeColors()refits the original image using the new colors (slow but often better results).mergeLayers()merges the layers of the existing recolored image. This is faster since it doesn't require a new fit, but can produce messier results.- ref_white
Reference white for converting to different color spaces. D65 (the default) corresponds to standard daylight.
- lower, upper
RGB triplet ranges for setting a bounding box of pixels to mask. See details.
- transparent
Logical. Treat transparent pixels as background? Requires an alpha channel (PNG).
- resize
A value between 0 and 1 for resizing the image (ex.
resize = 0.5will reduce image size by 50%). Recommended for large images as it can speed up analysis considerably. See details.- rotate
Degrees to rotate the image clockwise.
- plotting
Logical. Plot final results?
Value
An object of S3 class recolorize with the following attributes:
original_img: The original image, as a raster array.centers: A matrix of color centers in RGB (0-1 range).sizes: The number of pixels assigned to each color cluster.pixel_assignments: A matrix of color center assignments for each pixel.call: The call(s) used to generate therecolorizeobject.
Examples
# get image path
img <- system.file("extdata/corbetti.png", package = "recolorize")
# fit recolorize:
rc <- recolorize2(img, bins = 2, cutoff = 45)
#>
#> Using 2^3 = 8 total bins